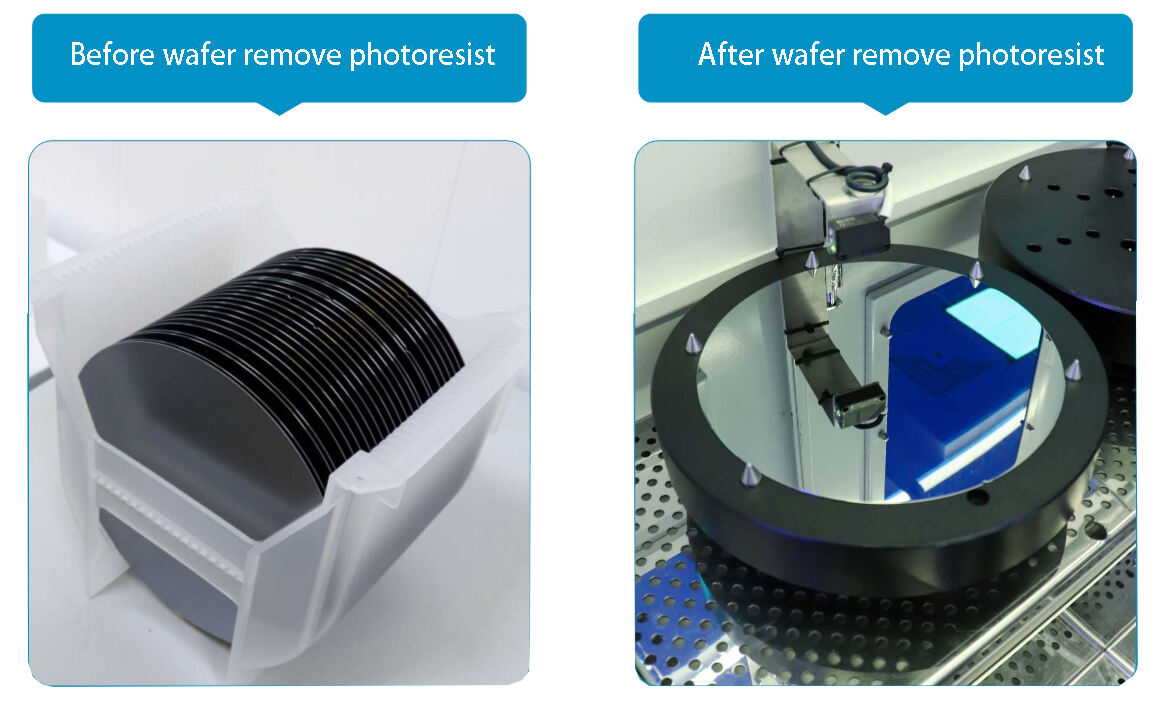
Why remove photoresist?
In modern semiconductor production processes, a large amount of photoresist is used to transfer circuit board graphics through the sensitivity and development of the mask and photoresist to the wafer photoresist, forming specific photoresist graphics on the wafer surface. Then, under the protection of the photoresist, pattern etching or ion implantation is completed on the lower film or wafer substrate, and the original photoresist is completely removed.
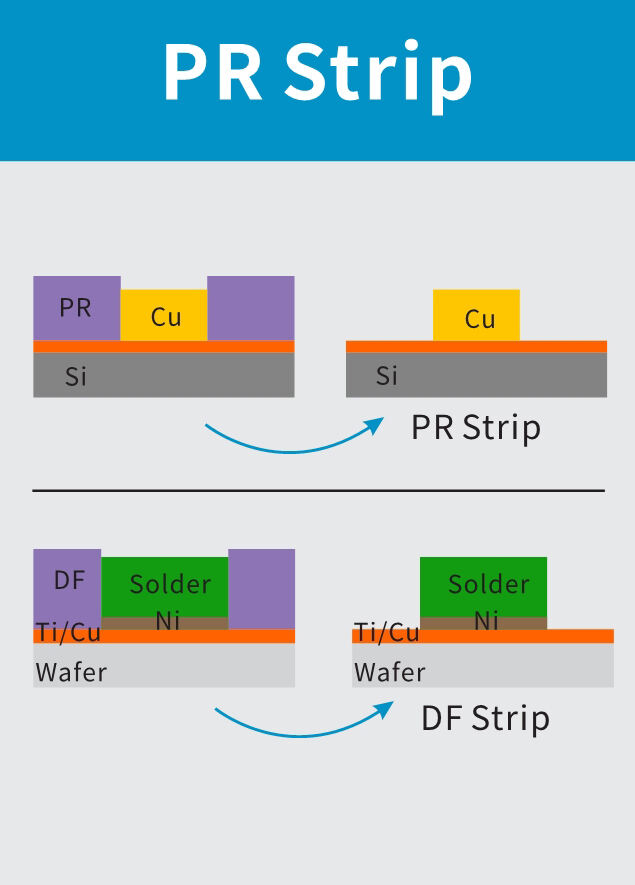
Degumming is the final step in photolithography. After the completion of graphic processes such as etching/ion implantation, the remaining photoresist on the wafer surface has completed the functions of pattern transfer and protective layer, and is completely removed through the debonding process.
The removal of photoresist is a very important step in the microfabrication process. Whether the photoresist is completely removed and whether it causes damage to the sample will directly affect the effectiveness of subsequent integrated circuit chip manufacturing processes.
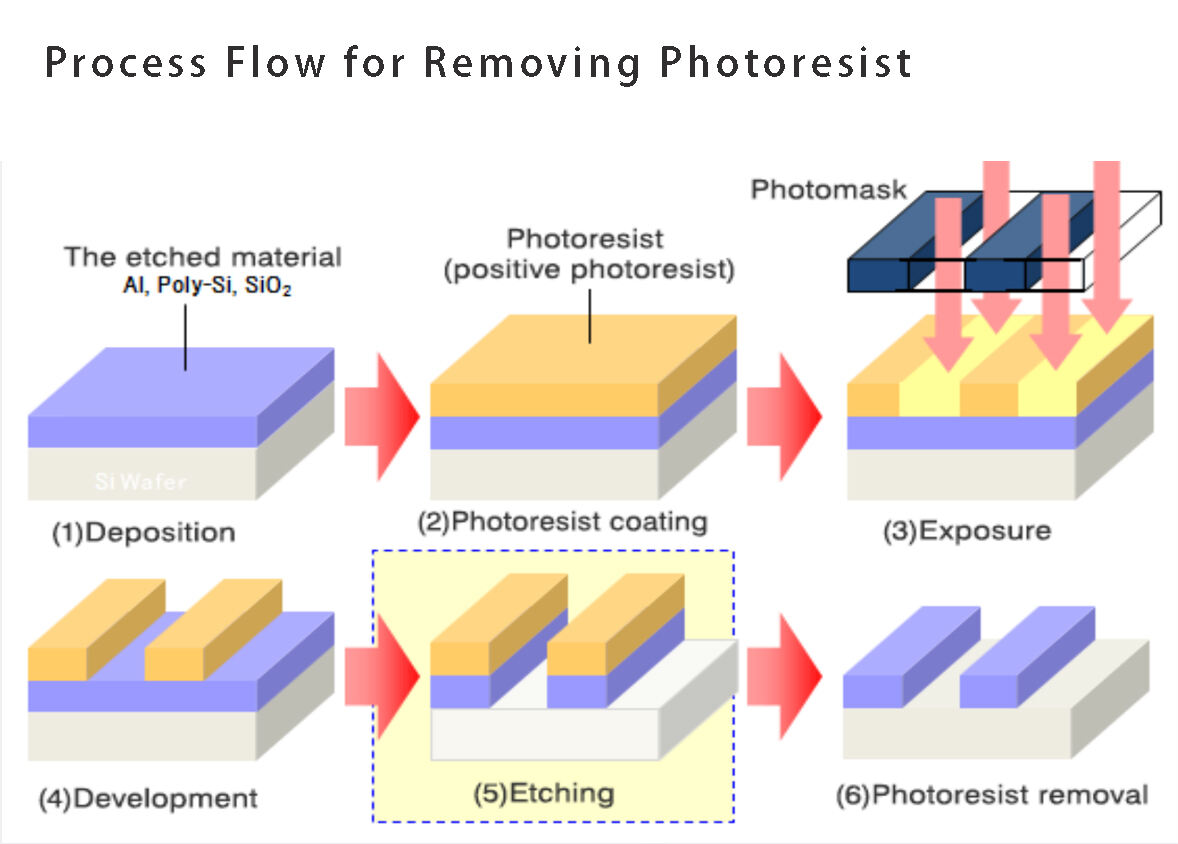
What are the processes for removing semiconductor photoresist?
The semiconductor photoresist removal process is generally divided into two types: wet photoresist removal and dry photoresist removal. Wet degumming can be divided into two categories based on the difference in the degumming medium: oxidation degumming and solvent degumming.
Comparison of various adhesive removal methods:
|
Degumming method |
Oxidative degumming |
Dry debonding |
Solvent degumming |
|
Main principles |
The strong oxidizing properties of H ₂ SO ₄/H ₂ O ₂ oxidize the main components C and H in photoresist to C0 ₂/H ₂ 0 ₂, thereby achieving the purpose of debonding |
Plasma ionization of 0 ₂ forms free 0, which has strong activity and combines with C in the photoresist to form C0 ₂. C0 is extracted by the vacuum system |
Special solvents swell and decompose polymers, dissolve them in the solvent, and achieve the purpose of degumming |
|
Main application areas |
Perishable metal, therefore not suitable for degumming in AI/Cu and other processes |
Suitable for the vast majority of debonding processes |
Suitable for debonding process after metal processing |
|
Main advantages |
The process is relatively simple |
Completely remove photoresist, fast speed |
The process is relatively simple |
|
Main Disadvantages |
Incomplete removal of photoresist, inappropriate process, and slow debonding speed |
Easy to be contaminated by reaction residues |
Incomplete removal of photoresist, inappropriate process, and slow debonding speed |
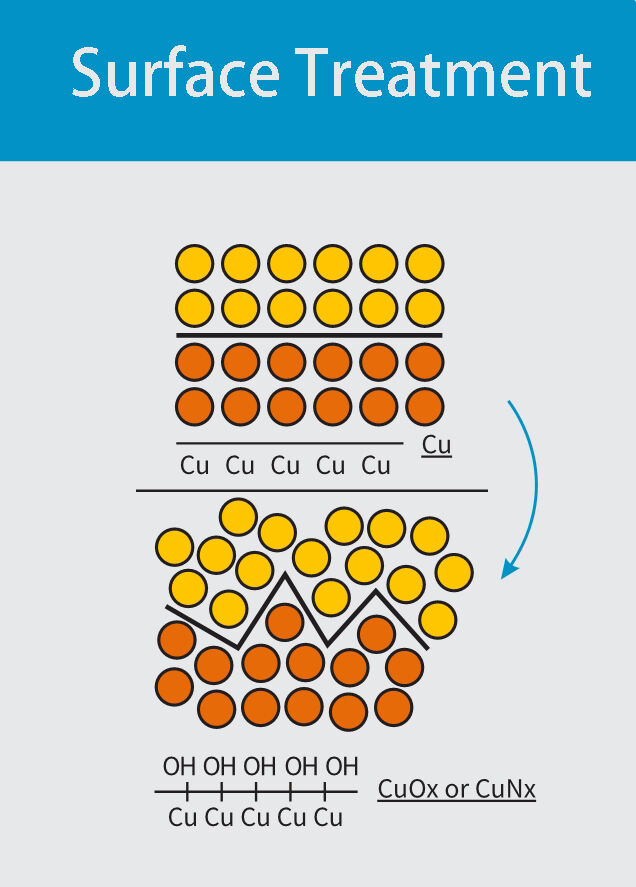
As can be seen from the above figure, dry debonding is suitable for most debonding processes, with thorough and fast debonding, making it the best method among existing debonding processes. Microwave PLASMA debonding technology is also a type of dry debonding.
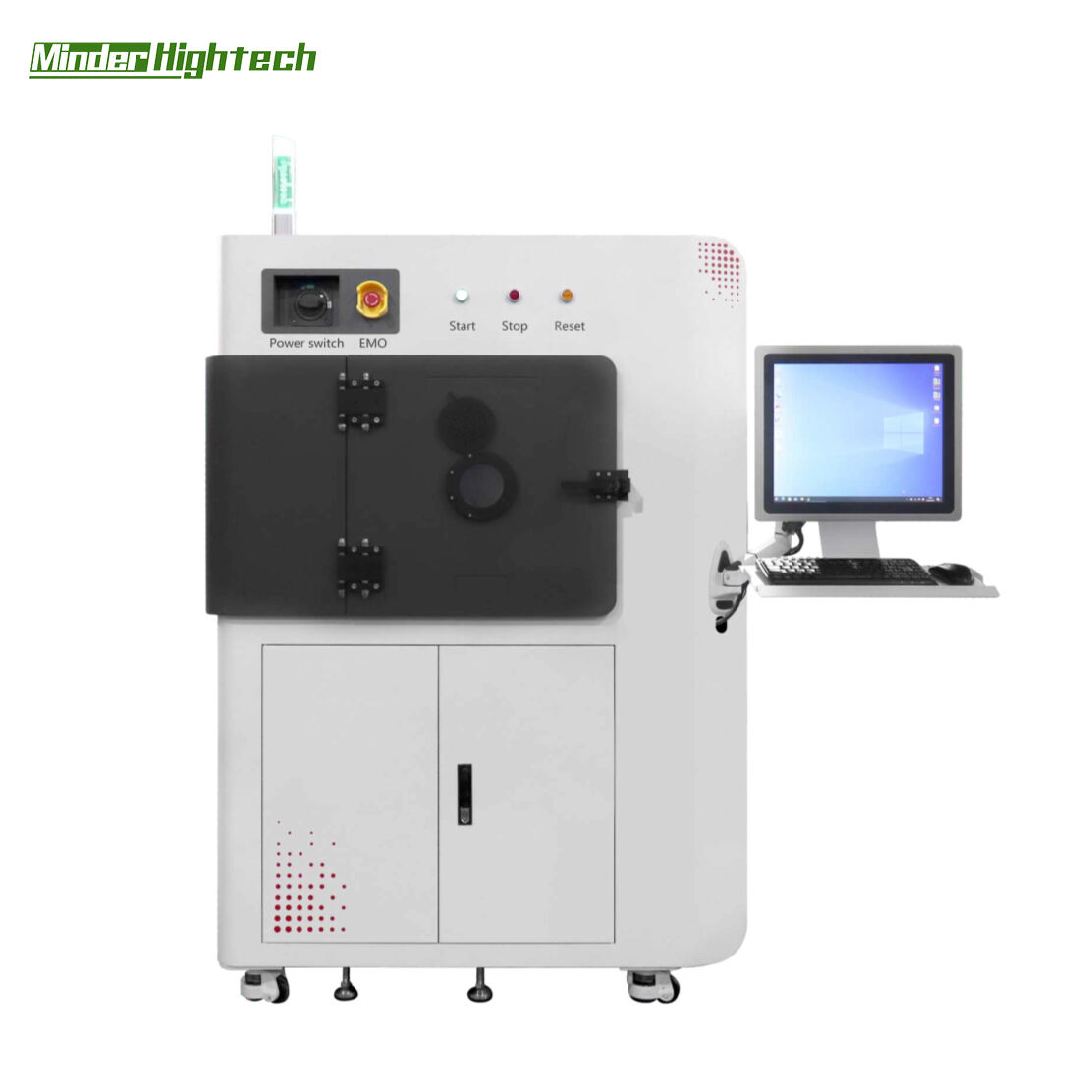
Minder-Hightech's microwave PLASMA debonding machine is equipped with the first domestic microwave semiconductor debonding generator technology, equipped with a magnetic fluid rotating frame, which makes the microwave plasma output more efficient and uniform. Not only does it have good debonding effect, but it can also achieve non-destructive silicon wafers and other metal devices. And provide "microwave+Bias RF" dual power supply technology to meet different customer needs.



Copyright © Guangzhou Minder-Hightech Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved